Ultimate Technical Guide to Industrial Plastic Welding Machines for Smart Manufacturing (2025 Edition)
Industrial plastic part assembly has entered a new era. From automotive bumper systems and HVAC ducts to plastic pallets, logistics containers, battery housings, IBC tanks, and consumer electronics enclosures, plastic welding machines have become the core manufacturing equipment enabling durable, leak-proof, and cost-efficient thermoplastic joining.
This comprehensive guide is engineered for manufacturing engineers, plant managers, automation designers, and procurement teams researching plastic welding machines, hot plastic welding machines, ultrasonic plastic welding machines, and related industrial joining technologies.
Published and continuously updated by Dizo Sonics, a global specialist in industrial welding automation, this document explains the science, equipment types, application selection logic, engineering design parameters, quality control requirements, and long-term maintenance strategies for high-performance thermoplastic welding systems.
1. Introduction: Why Plastic Welding Technology Matters in Modern Industry
Plastic materials such as PP, PE, HDPE, ABS, PC, PA, TPE, and PVC are replacing metals in structural product designs across industries due to weight reduction, corrosion resistance, cost efficiency, and recyclability. However, assembly remains a technical challenge, especially when products demand airtight sealing, high mechanical strength, vibration resistance, or precision tolerances.
This is why technologies such as plastic welding machines, hot plate plastic welding machines, ultrasonic plastic welding machines, infrared plastic welding machines, vibration welders, and spin welders have become indispensable. They provide thermal bonding at molecular level—without adhesives or mechanical fasteners—leading to:
- Strong and hermetic joints
- No consumable glue or metal screws
- Short cycle time suitable for automation
- High repeatability and weld quality
- Ability to weld large parts such as pallets & bumpers
These benefits are critical for industries including automotive, logistics, packaging, home appliances, medical products, and energy storage.
Refer to real industrial case examples here:
Plastic Welding Machine Case Studies
2. Overview of Plastic Welding Technologies
Thermoplastic welding methods can be classified based on heat generation mechanism:
| Technology | Heating Method | Typical Applications | Machines |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot Plate Welding | Conductive thermal contact | Large PP/PE/HDPE parts | Hot plate plastic welding machine |
| Ultrasonic Welding | High-frequency vibration | Small precision parts | Ultrasonic plastic welding machine |
| Vibration Welding | Linear friction heat | Medium automotive parts | Vibration plastic welding equipment |
| Infrared Welding | IR radiation heating | High cosmetic quality parts | Infrared plastic welding machines |
| Spin Welding | Rotational friction heat | Round connectors/tanks | Plastic spin welding machine |
Learn about industrial use cases here:
Plastics Industry Association
3. Hot Plate Plastic Welding Technology: Engineering Fundamentals
Hot plate welding is preferred for large, load-bearing thermoplastic assemblies where structural strength and airtight sealing are critical. Typical welded products include:
- Plastic pallets (PP, HDPE)
- Large storage crates and bins
- Automotive HVAC housings
- Automotive bumpers and dashboard supports
- Battery housings
- Water tanks & fuel tanks
A hot plastic welding machine uses a controlled heated plate to soften mating surfaces, followed by pressure joining under precision motion control. The weld relies on polymer chain diffusion, producing a joint as strong as virgin material.
3.1 Key Engineering Parameters in Hot Plate Welding
- Plate temperature: 180–350°C depending on polymer type
- Soak time controlled by thickness & melt flow index
- Clamping force precision ±2%
- Servo pressure and travel control for premium systems
- Cooling and solidification cycle management
Reference standard:
ISO 21307: Plastic welding — Standard welding procedures
3.2 Advantages of Hot Plate Welding Machines
- Welds very large parts
- Extremely strong structural joints
- Compatible with PP/PE/HDPE where ultrasonic struggles
- Smooth seam, suitable for painted & cosmetic parts
- Better seal integrity than screws or adhesives
Try industrial demo with:
Request Technical Evaluation
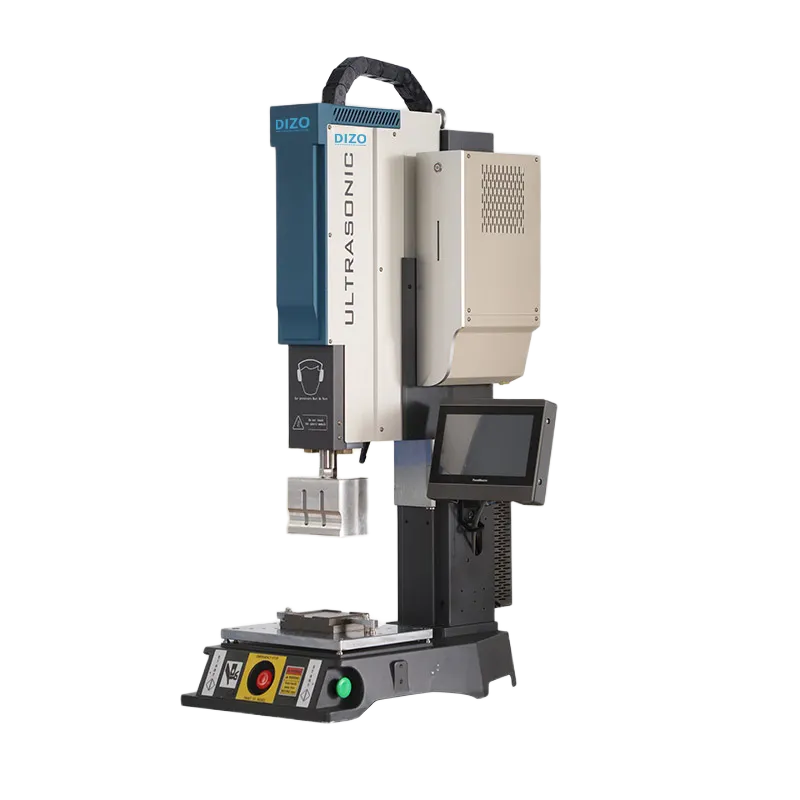
4. Ultrasonic Plastic Welding: When Vibration Meets Precision
The ultrasonic plastic welding machine uses high-frequency mechanical vibration (typically 20–40 kHz) to generate internal heat in plastics. It is the most widely used method for small-to-medium precision parts.
Typical applications:
- Electronics housings
- Automotive sensors & small components
- Medical device housings
- PVC filters
- Consumer device casings
- Battery safety vent valve welding
Explore ultrasonic systems here:
Ultrasonic Plastic Welding Machines
5. Infrared Plastic Welding Machines: Clean & Contactless
Infrared welding relies on electromagnetic radiation absorption by polymer molecules. It eliminates contact marks and contamination risk, making it ideal for visible components or sensitive assemblies.
Advantages:
- No direct plate contact
- Cosmetic weld finish
- Shorter cleaning downtime
- Cleaner process for EV battery cases & medical parts
6. Plastic Pallet Welding Machines: Industrial Case Study
High-load industrial pallets (PP/PE) require thick rib-reinforced structures and high joint strength. This is where hot plate pallet welding machines excel.
Explore:
Plastic Pallet Welding Machine
Advantages:
- Strong reinforcement rib fusion
- Automated pallet clamping
- Servo movement control
- Precision pressure feedback
- Better durability than mechanical fastening
7. Contact Dizo Sonics Engineering Team
For real-world factory consultation, joint testing, or project bidding:
📩 Request Engineering ConsultationEmail: sales04@nicle.cn | WhatsApp: +86 15358007790
Next Sections Preview (Will Output If You Reply)
- Material science of thermoplastics for welding
- Servo motion vs pneumatic systems
- Melt flow index tables and selection
- Energy directors, joint design geometry
- Cycle time engineering calculation
- Automation robotics integration
- Maintenance & spare part lifecycle
- Industrial safety standards and ISO compliance
- Plant-layout architecture for pallet welding lines
- Real case study: Automotive bumper vs pallet welding
Hot Plate Welding for Complex Industrial Plastic Assemblies
In advanced industrial manufacturing, plastic components often include ribs, bosses, multi-layer structures, and reinforced geometries. Hot plate welding is especially effective for these parts because it creates strong hermetic joints without weakening reinforced structures. Compared to ultrasonic welding, which may struggle with high mass components or glass–fiber reinforced plastics, hot plate welding offers superior adaptability and deeper fusion depth.
Ideal Applications
- Car interior and exterior structural plastic assemblies
- ABS and PP reinforced components
- Thick-wall engineered plastic housings
- Plastic pallets and logistics containers
- White-goods structural components
- HVAC plastic duct manifolds
- Battery protective enclosures
For example, automotive instrument panel carriers, crash-safety plastic brackets, and EV battery cooling components require high-precision structural welding capability. Hot plate welding machines deliver consistent weld penetration and strength needed to meet OEM and Tier-1 supplier specifications.
Ask Engineer for Free Technical Advice →Hot Plate Welding vs Infrared Welding
| Parameter | Hot Plate Welding | Infrared Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Transfer Method | Direct physical heating contact | Non-contact IR radiation |
| Cycle Time | Moderate | Faster |
| Weld Appearance | Excellent, controlled melt bead | Excellent, ultra-clean edges |
| Part Sensitivity to Contamination | Low | Low |
| Best For | High-strength structural parts | Premium aesthetic, complex shapes |
Manufacturers producing automotive decorative components, water-tight medical housings, or EV battery cooling channels often consider infrared welding. However, for heavy-duty structural assemblies, hot plate welding remains the global industry benchmark.
Request IR vs Hot Plate Comparison Guide →PLC & Motion Control Technology in Hot Plate Welding Machines
Modern hot plate plastic welding machines incorporate intelligent motion systems to maintain precision under industrial automation conditions. DZSONICS systems use servo controls, closed-loop pressure monitoring, and adaptive welding algorithms to optimize every weld cycle. This ensures repeatability, low scrap rate, and long-term welding stability.
Smart Welding Controls
- Servo-controlled welding axes (X/Y/Z)
- Welding pressure PID feedback loops
- Digital heater temperature calibration
- Displacement and pressure traceability
- AI-assisted melt depth prediction (2025 update)
These control features support Industry 4.0 manufacturing and MES connectivity. Engineering teams responsible for quality validation appreciate integrated welding curve data and PLC-based digital signatures.
Download Welding Control System Whitepaper →Hot Plate Welding Machine Applications in Logistics Packaging Industry
The global logistics packaging market increasingly relies on plastic pallets, foldable crates, and reusable transport containers. Thick-wall HDPE & PP components require deep fusion strength and airtight joints. Hot plate welding machines provide the most reliable assembly method for these products.
Common Logistics Products Welded by Hot Plate Machines
- Industrial plastic pallets
- Foldable bins and storage crates
- Returnable plastic packaging (RTP)
- IBC container accessories
Related reference: Plastic pallet welding machine
Global brands in automotive supply chain logistics increasingly adopt welded heavy-duty pallets to replace nails, screws, or metallic brackets, achieving stronger load performance and improved hygienic design.
Get Free Pallet Welding Technical Guide →Case Studies: Customer success cases
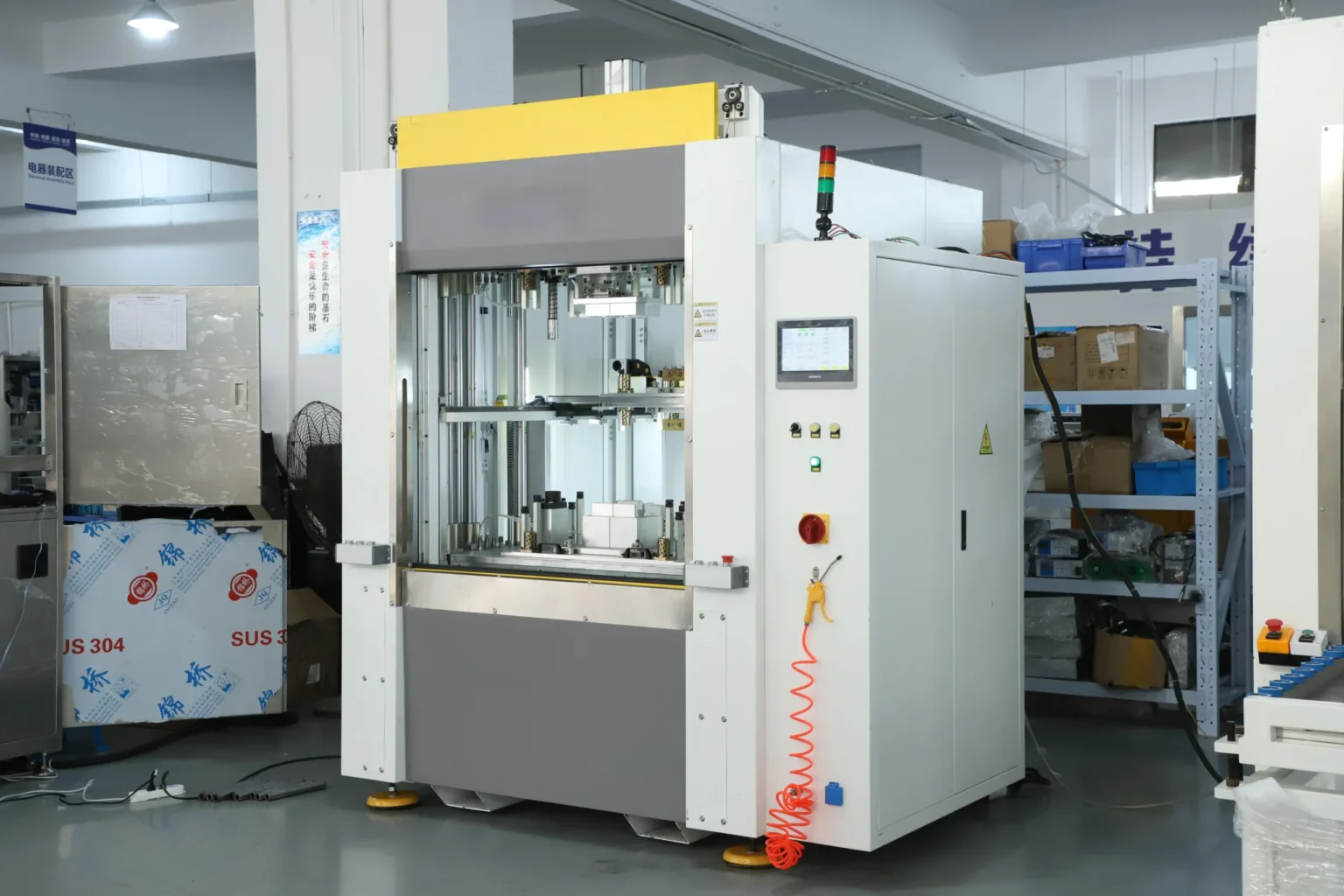
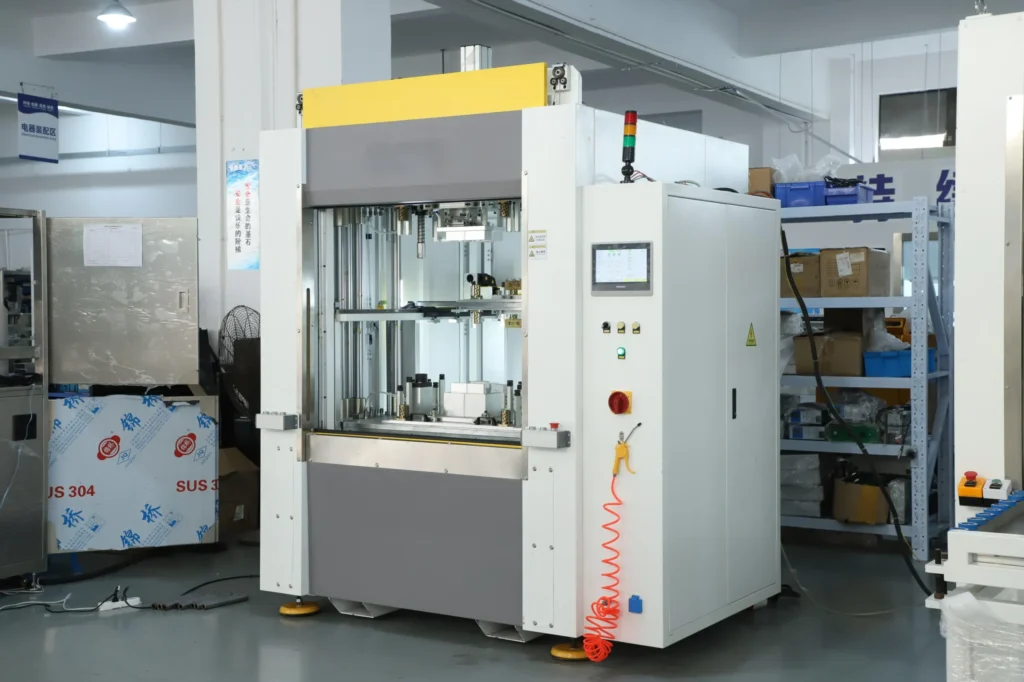
Hot Plate Welding Machine Mechanical Structure & Engineering Design
A high-performance hot plate welding machine is not simply a heating table with motion systems. It is a precision engineered system designed for repeatable thermoplastic joining under manufacturing conditions. Structural rigidity, synchronized motion control, and repeatable temperature management make the difference between consistent industrial welds and unstable assemblies.
Core Structural Components
- Heavy-duty steel frame, vibration-resistant
- Servo-driven vertical and horizontal motion units
- Precision linear guide rails
- Closed-loop pneumatic or hydraulic clamping system
- High-precision heating plate modules
- Digital temperature and pressure control units
Machine durability and accuracy are critical when welding structural automotive and logistics components. High-mass plastic assemblies require strong support frames to avoid thermal and mechanical distortion across thousands of cycles. A poorly-designed machine results in joint failure, deformation, or dimensional drift.
Reference industrial solution: Automatic hot plate welding machine
Request Detailed Machine Drawing & Specification →Hot Plate Heating System Engineering
The heating module is the heart of the machine. The objective is to achieve uniform melting on both surfaces, controlled by digital temperature regulation, thermal feedback loops, and thermal compensation logic.
Key Heating Specifications
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 100°C – 450°C |
| Heating Tolerance | ±1°C digital closed-loop control |
| Heating Surface Material | Aluminum alloy / high-temperature steel |
| Surface Coating | PTFE / Ceramic / Hard oxidation |
| Heating Zone Control | Multi-zone PID independent control |
For advanced engineered plastics such as glass-fiber reinforced PP, PA6, or PBT materials, controlling the heat penetration and melt layer thickness is critical to structural joint integrity. Inconsistency leads to internal stress, delamination, or premature cracking during mechanical load or vibration testing.
Learn more about plastic welding material science: Plastic welding technology knowledge base
Get Free Material Welding Temperature Chart →Cooling, Clamping, and Fusion Pressure Control
Cooling and clamping phases determine the dimensional accuracy and final weld strength. Industrial-grade systems implement servo pressure curves and high-precision cooling cycles to ensure controlled crystallization and material stabilization.
Pressure Control Features
- Servo-controlled pressure profiles
- Real-time pressure feedback sensors
- Programmable holding time
- Multi-stage clamping sequence
- Automatic tolerance correction
Clamping fixtures are custom-engineered for each part to ensure perfect alignment. Precision fixture design differentiates mass production success from prototype-grade assembly.
Fixture design reference: Hot plate welding fixtures
Request Free Fixturing Consultation →Hot Plate Welding Process Parameters
Process optimization is key for maximizing weld strength, minimizing cycle time, and ensuring repeatable quality. Below are standard configuration factors.
Key Parameters
- Temperature range: 185°C–350°C (material dependent)
- Melt penetration depth: 0.4–2.2 mm typical
- Fusion pressure: 0.4–6.0 MPa
- Holding time: 2–15 seconds
- Cycle time: 15–35 seconds
These values are refined through DOE process development. For sensitive parts, machine learning-assisted parameter optimization now helps shorten validation time (2025 industry trend).
Download Standard Welding Parameter Table →
Hot Plate Surface Coating Technology & Anti-stick Engineering
During hot plate welding, molten polymers can adhere to metal heating surfaces if surface conditioning is not properly engineered. Advanced coating technologies improve heat transfer, material release, and machine longevity. Dizo Sonics implements industry-grade release coatings refined for automotive and logistics-grade thermoplastics.
Common Hot Plate Surface Coatings
| Coating Type | Advantages | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| PTFE (Teflon) | Excellent release, low adhesion, low friction | PP, HDPE, ABS pallet and automotive trim welding |
| Ceramic-oxide | Durability, temperature uniformity, scratch resistance | High-volume OEM automotive parts |
| Titanium surface plating | High strength, thermal stability | Thick-wall engineering plastic components |
| Hard anodized aluminum | Cost-effective, reliable temperature conduction | General industrial plastic assemblies |
Surface engineering prevents polymer residue accumulation, improves weld uniformity, and extends heater lifespan. Surface temperature uniformity must be validated with thermal imaging systems during commissioning for precision melting behavior.
Professional hot plate design resources: Dizo Sonics fixture & hot plate engineering service
Request Heating Plate Material Whitepaper →Thermoplastic Material Science for Hot Plate Welding
Hot plate welding performance strongly correlates with polymer molecular structure, melt flow index, crystallinity, filler content, and thermal degradation behavior. Understanding resin science enables predictable weld strength and product lifetime performance.
Common Plastics in Industrial Hot Plate Welding
- Polypropylene (PP, PP-GF30)
- Polyamide (PA6, PA66, PA-GF)
- Acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS)
- Polyethylene (HDPE / UHMW-PE)
- Glass fiber-reinforced composites
- PC/ABS automotive blends
Crystalline polymers like PP and PA require precise melt layer control and cooling pressure programs to stabilize spherulite formation and reduce internal stress. Reinforced materials (GF composites) require optimized clamping to avoid fiber pull-out.
Material engineering reference: Advanced plastic welding material science
Access Welding Material Compatibility Chart →Quality Defects & Failure Modes in Hot Plate Welding
Understanding weld failure modes helps manufacturers design robust assembly processes. Below are critical defect categories in thermoplastic hot plate fusion systems.
Typical Failure Modes
- Insufficient melt depth
- Over-melt and geometry collapse
- Fiber exposure (GF parts)
- Cold joint formation
- Misalignment / positional shift
- Voids & micro-bubble formation
- Stress whitening / stress cracking
- Thermal degradation / odor / discoloration
Weld joint quality must be validated via tensile strength tests, destructive pull-testing, and thermal cycling. Dizo Sonics supports on-site parameter calibration and validation.
Case studies:
Schedule Free Weld Failure Analysis Consultation →Industrial Applications of Hot Plate Welding Machines
Hot plate welding is widely used in automotive, logistics, medical, consumer product, and energy storage manufacturing. Applications include large structural components requiring strong, hermetic bond lines.
Industry Applications
- Plastic pallet & logistics container welding
- Automotive exterior and interior modules
- Coolant & fluid tanks
- Washer fluid reservoirs
- Luggage & consumer case products
- Energy storage battery casings
- Seating and console assemblies
- Large PP / PE engineering structures
Cross-technology comparison at Dizo Sonics: Hot plate welding systems | Ultrasonic welding machine | Vibration welding machine
Get Free Application Report for Your Product →AI-Enhanced Hot Plate Welding Control Systems (2025 Industrial Trend)
Modern factories leverage machine learning to predict optimal weld parameters, detect defect patterns, and enhance operator decision-making. AI-integrated welding platforms use sensor fusion, vibration monitoring, and surface temperature mapping to guarantee repeatable quality.
AI-Driven Process Enhancements
- Real-time heating profile correction
- Cycle time optimization algorithms
- Weld quality prediction models
- Servo pressure curve learning
- Camera-based joint melt depth monitoring
- Energy optimization based on part geometry
Dizo Sonics integrates predictive control modules and industrial IoT analytics to support future smart welding ecosystems.
Smart welding solutions: Dizo Sonics intelligent welding technology
Request Industry 4.0 Welding Demo →Hot Plate Welding Standards, Certification & Compliance
Industrial welding equipment must meet ISO, automotive, and safety certification standards. Dizo Sonics adheres to global compliance frameworks for machine qualification, traceability, and safety certification.
Relevant Standards
- ISO 19014 — Machinery safety
- IATF 16949 — Automotive quality management
- ISO 16792 — 3D CAD data exchange
- CE / UL machine safety compliance
- IEC 60204 — Electrical safety
- RoHS / REACH compatible materials
Documentation support is included for factory audit readiness and equipment validation.
Request Compliance Documentation Package →Advanced Hot Plate Welding Parameter Engineering & Control Logic
Modern hot plate welding machines from Dizo Sonics are engineered with multi-loop control systems and real-time thermal compensation algorithms. Traditional fixed-profile welding is no longer sufficient for complex polymer structures, particularly in automotive, logistics, and energy applications.
Parameter Domains in Hot Plate Welding
A robust welding process requires calibration across multiple parameter layers, including thermal, mechanical, and dynamic controls:
- Plate temperature (multi-zone, ±1.5°C control)
- Melt penetration depth (mm precision measurement)
- Displacement / stroke control
- Servo pressure profile & ramp curve
- Cooling profile under load
- Surface contact geometry design
- Humidity, environmental temperature, material batch variables
At Dizo Sonics, welding machines incorporate thermal feedback loops, servo pressure adjustment, and multi-sensor distributed data acquisition to ensure optimal weld fusion. For reference: Hot Plate Welding Systems
Parameter Optimization Workflow
- Material rheology & crystallinity evaluation
- Pre-heating and thermal conditioning sequences
- Melt layer formation analysis
- Bond consolidation timing study
- Cooling compression phase validation
- Destructive strength validation (pull/bend/impact tests)
A structured parameter development approach reduces cycle time and increases structural strength by up to 20-40%, especially in automotive and pallet welding projects.
Request Hot Plate Welding Parameter Audit →Weld Intelligence & Process Monitoring Framework
A modern plastic welding line requires real-time intelligence to guarantee quality. Dizo Sonics applies Industry 4.0 monitoring and machine learning logic to stabilize weld output.
Key Sensors in Smart Welding Platforms
- Thermocouple grid sensors (hot plate)
- Laser displacement sensors for melt depth
- Pressure transducers for force signature tracking
- Servo position feedback encoders
- Infrared weld surface thermal mapping
- Vibration signal logging during cooling compression
Data collected from sensors supports predictive welding control. For advanced technology info: Dizo Sonics Smart Welding Technology
Get Predictive Welding Intelligence Guide →Thermal Dynamics & Polymer Melt Layer Science
The science of polymer melting is critical for advanced hot plate welding. A plastic part’s strength is directly related to molecular diffusion across melt layers.
Molecular Bonding Mechanisms
- Surface molecular mobility
- Polymer chain diffusion & entanglement
- Crystalline re-formation in PP/PA
- Amorphous structure relaxation (ABS/PC-ABS)
Poor melt control causes cold welds or material burn-off. Dizo Sonics engineers optimize melt diffusion window based on polymer structure and reinforcement content.
Request Polymer Melt Analysis Support →Failure Prevention & Engineering Inspection Protocols
Engineers need structured validation routines to avoid field failures. Below is a recommended test matrix for hot plate welded components.
Mechanical Tests & Qualification
- Tensile pull test (ASTM D638-modified)
- Flexural stress test
- Drop impact test (plastic pallet industry)
- Pressure leak test for reservoirs
- Environmental chamber cycling
- Vibration & mechanical fatigue exposure
Long-cycle reliability testing is essential for automotive welding and logistics container manufacturing. Case library: Dizo Sonics Welding Case Studies
Request Weld Inspection Standard Templates →Industrial Case Studies: Automotive + Logistics + Energy
Below are representative industrial use cases where Dizo Sonics hot plate welding technology delivers measurable performance improvements.
Case 1: Automotive Washer Tank Assembly
Outcome: Improved leak-free rate from 97.2% → 99.85% Cycle time reduced by 11% using AI-based heat control and servo compression.
Case 2: Heavy-Duty HDPE Pallet Manufacturing
A global logistics firm migrated from vibration welding to hot plate welding for 3-runner pallets and double-deck hygiene pallets.
- Strength improvement: +38% load strength
- Cycle time reduction: −22%
- Scrap reduction: −17%
- Payback period: 6 months
Machine reference: Plastic Pallet Hot Plate Welding Machine
Case 3: Energy Storage Housing
Cell battery cases requiring hermetic sealing achieved consistent thermal fusion with real-time pressure feedback control.
Discuss Your Project with Our Engineers →Industrial Knowledge Base & Engineering FAQs
Below is a structured FAQ section designed for engineers, purchasing managers, and manufacturing directors evaluating hot plate welding.
Engineering FAQs
- How to select the correct heating profile for PP vs PA?
- What surface preparation improves weld repeatability?
- How does fiber-reinforced polymer welding differ?
- How to prevent weld flash and dimensional collapse?
- What sensor configuration maximizes quality consistency?
- How to reduce cycle time without reducing weld strength?
- What AI logic improves real-time weld accuracy?
- What is the recommended process documentation framework?
Full engineering FAQ library available: Dizo Sonics Welding Knowledge Base
Access 100+ Welding Optimization Guides →Hot Plate Welding Machine for EV Battery Plastic Components
The rapid expansion of electric vehicles demands precision-sealed plastic components in high-voltage battery assemblies. Hot plate welding machines are widely used for battery pack covers, cooling manifolds, high-voltage connector housings, sensor mounts, and sealing frames.
| Requirement | Why Hot Plate Welding Works |
|---|---|
| Airtight sealing | Prevents electrolyte and moisture ingress |
| Vibration resistance | Meets automotive durability standards |
| High temperature performance | Survives thermal cycling in EV systems |
| Dimensional accuracy | Servo fixtures + CNC plate motion |
| Zero-residue & no adhesives | Long lifecycle, no adhesive aging |
Engineers choose hot plate welding for EV plastics because it provides consistent, structural, and hermetic assembly—especially compared to adhesives or mechanical fasteners. See our engineering posts at Dizo Sonics Blog.
Hot Plate Welding vs Infrared Welding — Technical Comparison
| Feature | Hot Plate Welding | Infrared Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Transfer | Direct contact conductive heating | Non-contact IR radiation |
| Surface Quality | Possible plate imprint (managed by coating) | No contact marks; excellent cosmetic finish |
| Cycle Time | Medium | Often faster |
| Capital Cost | Lower / standard | Higher (IR optics & control) |
| Best For | Thick/structural parts | Thin/cosmetic parts |
Infrared welding is effective for thin-wall and cosmetic applications, while hot plate welding remains the go-to for heavy/large structural components because of its melt depth capability and cost-effectiveness.
Design-for-Weld (DFW) Rules for Engineers
Design-for-Weld (DFW) is a set of practices that make parts easier and more reliable to weld. Following DFW reduces rejects and simplifies fixturing and cycle validation.
Key DFW Considerations
- Choose joint geometry that supports thermal flow: tongue-and-groove, shear joints, and flash traps
- Maintain minimum weld thickness: typically 2.5–3.0 mm at the weld interface
- Design for uniform wall thickness near the weld to avoid hot spots and warpage
- Avoid placing metal inserts directly across the weld line
- Provide venting or escape routes for trapped air and gases
- Locate mold gates and ribs to minimize stress concentration at the weld
Recommended Joint Example
┌────────────┐ | Plastic A | ← Flash-trap cavity └──┬──────┬──┘ | Weld | ← Weld interface zone ┌──┴──────┴──┐ | Plastic B | └────────────┘
Following these DFW rules will improve first-pass yield and reduce the need for secondary machining or trimming.
Quality Control Tests for Hot Plate Welded Parts
Implement a robust testing matrix to qualify weld integrity before production sign-off. Typical tests include:
- Visual inspection — detect flash, burns, or surface imperfections
- Ultrasonic leakage test — air-tightness and hidden void detection
- Pressure decay test — leak validation for tanks/reservoirs
- Drop test — mechanical durability for pallets/crates
- Tensile pull test — measure joint strength
- Thermal cycling — aging and lifetime performance
- CT scan / weld cross-section analysis — internal weld structure verification
Automated options include vision-based defect detection, force signature monitoring during weld, and AI-based surface anomaly recognition. For templates and test plans, request our inspection package: Request Inspection Templates.
Typical Industries and Use-Cases
Hot plate welding is used across many industries. Representative sectors include:
- Automotive & Tier-1 suppliers
- EV battery & thermal systems
- Household appliances
- Water filtration & fluid handling
- Medical devices & lab equipment
- Logistics & industrial packaging (plastic pallets & crates)
- Consumer electronics housings
Explore industry-specific solutions here: Industrial Applications — Dizo Sonics.
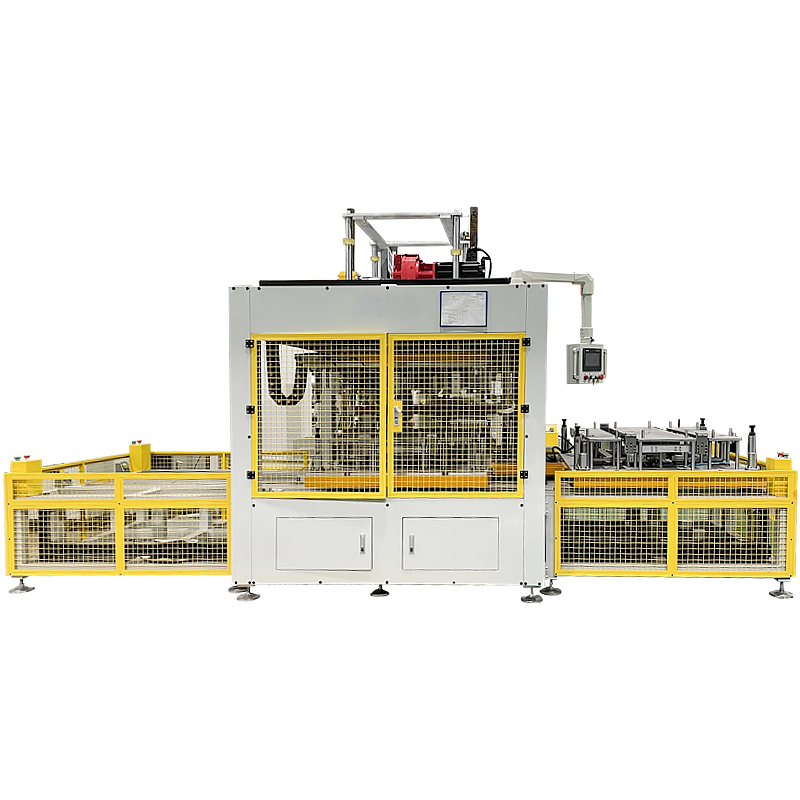
Automation Options & Industry 4.0 Integration
Automation reduces variability and increases throughput. Common automation layers in hot plate welding lines:
- Servo-driven presses for deterministic motion and force control
- Robotic part loading/unloading (6-axis or gantry robots)
- Automated fixture exchange for multi-model production
- Barcode / RFID traceability per part
- MES / ERP integration for production scheduling and data logging
- Cloud analytics for predictive maintenance and energy optimization
Examples of automation integration: weld curve logging, per-part traceability, and automated QC gating using AI-enabled camera inspection. Learn more about smart welding systems at Dizo Sonics Technology.
Why Choose Dizo Sonics Hot Plate Welding Machines
Dizo Sonics combines decades of plastic welding expertise with servo motion control and modern Industry 4.0 features. Key differentiators:
- Specialization in automotive, pallet, and EV battery welding systems
- In-house CNC machining and precision heating plate manufacturing
- PLC + servo systems for repeatable cycle control
- Global commissioning, training and after-sales support
- Compliance with ISO and automotive standards; full documentation support
Typical machine durability: 10+ years with scheduled preventive maintenance. Standard warranty and extended service packages are available. View machine categories at Dizo Sonics Products.
Contact & Support
If you would like machine selection help, joint design consultation, fixture design, or a sample welding test, contact us:
Email: sales04@nicle.cn
WhatsApp: +86 15358007790
Contact page: https://dzsonics.com/en/contact-us/
Note: For detailed project evaluation please provide part drawings, material data sheets, and target cycle time. Our engineers will return a feasibility report and proposed parameters.